What really causes Eczema
Your skin has two main layers: A thin outer layer called the epidermis and a thick inner layer called the dermis.
Eczema affects the outer layer. People suffering with Eczema have a slightly thinner outer layer of skin than others. This outer layer is a sheet of flattened dead cells that are constantly pushed up from the inside.
Adults and children with Eczema lose this protective acid layer and bacteria & toxins from the environment get access to deeper layers of the skin where they don’t belong.
The immune system recognizes this threat and begins to attack these toxins in the skin by causing inflammation.
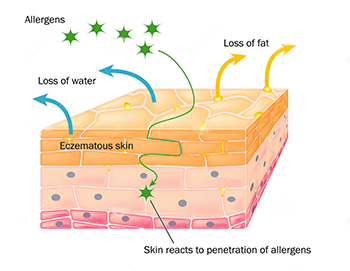
-
Naturally thin skin causes sensitivity to environmental toxins
-
Skin loses its protective acid mantle layer
-
Bad bacteria & allergens get access to deeper layer skin
-
The immune system becomes alarmed & attacks these irritants
-
Skin becomes inflamed & irritated
Unfortunately, since the protective barrier is lost, the toxins constantly keep getting deeper access to your skin and the immune system never rests.
The result is severe drying, itching & flaking of the skin that keeps recurring.
The only way to stop this constant damage to your skin is to rebuild the lost barrier on the epidermis, allowing your immune system to rest and the skin to heal itself.
